Ensuring A Cool & Safe Environment
The World Health Organization estimates that heat exposure contributes to over 150,000 deaths annually worldwide. As temperatures rise, the risk of heat-related illnesses becomes a significant concern for both employers and employees. Recognizing the importance of creating a safe and comfortable working environment, this guide aims to provide valuable insights, tips, and strategies to prevent heat stress and promote well-being at the workplace.
Understanding Heat Stress
What is Heat Stress?
Heat stress occurs when the body’s cooling mechanisms are unable to regulate internal temperature effectively. Prolonged exposure to high temperatures, combined with humidity and physical exertion, can lead to various heat-related illnesses. These illnesses range from mild conditions like heat rash to severe and life-threatening issues such as heat stroke or even death.

Factors Contributing to Heat Stress
Several factors contribute to the risk of heat stress in the workplace:
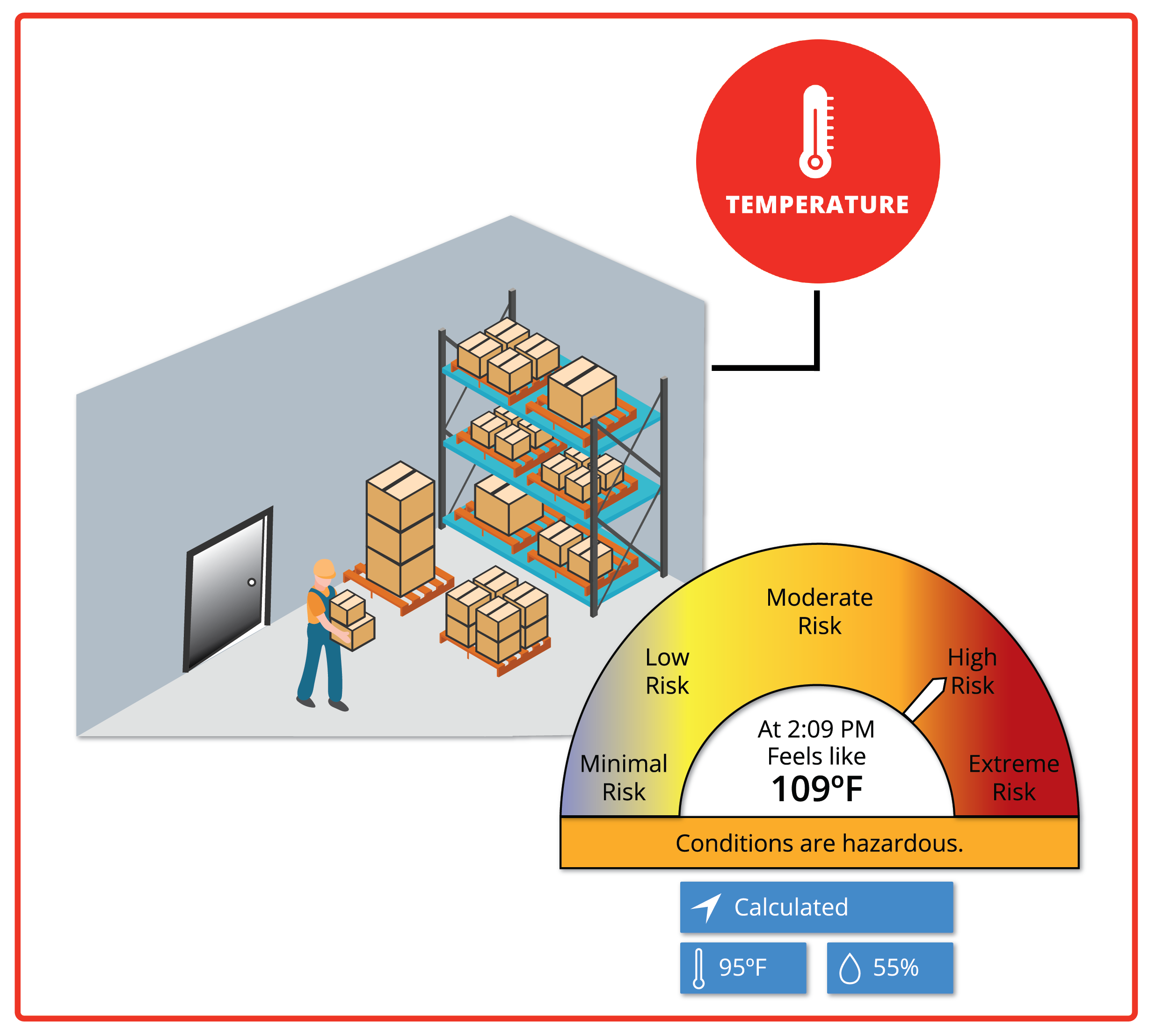
Temperature | High ambient temperatures are an obvious risk factor. However, radiant heat sources, such as machinery & equipment, can also significantly impact the working environment. |
Humidity | High humidity reduces the body's ability to cool itself through sweating. In humid conditions, sweat does not evaporate as quickly, making it harder for the body to release heat. |
Heat Index | Heat Index is the “feels like” temperature that helps us interpret how the heat and humidity affects how the temperature feels to the human body. The amount of moisture in the air affects the body’s ability to dissipate heat. For example, on a day with high humidity, the “feels like” temperature might be quite a bit warmer than the actual temperature. The Heat Index will reflect the actual condition that your employees are working in. |
Physical Exertion | Manual labor, intense physical activity, or prolonged periods of standing can increase the body's heat production, adding to the risk of heat stress. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Wearing certain types of PPE, such as heavy clothing or equipment, can contribute to heat stress by impeding the body's ability to cool down. |
Hydration | Inadequate fluid intake can lead to dehydration, making the body more susceptible to heat stress. |
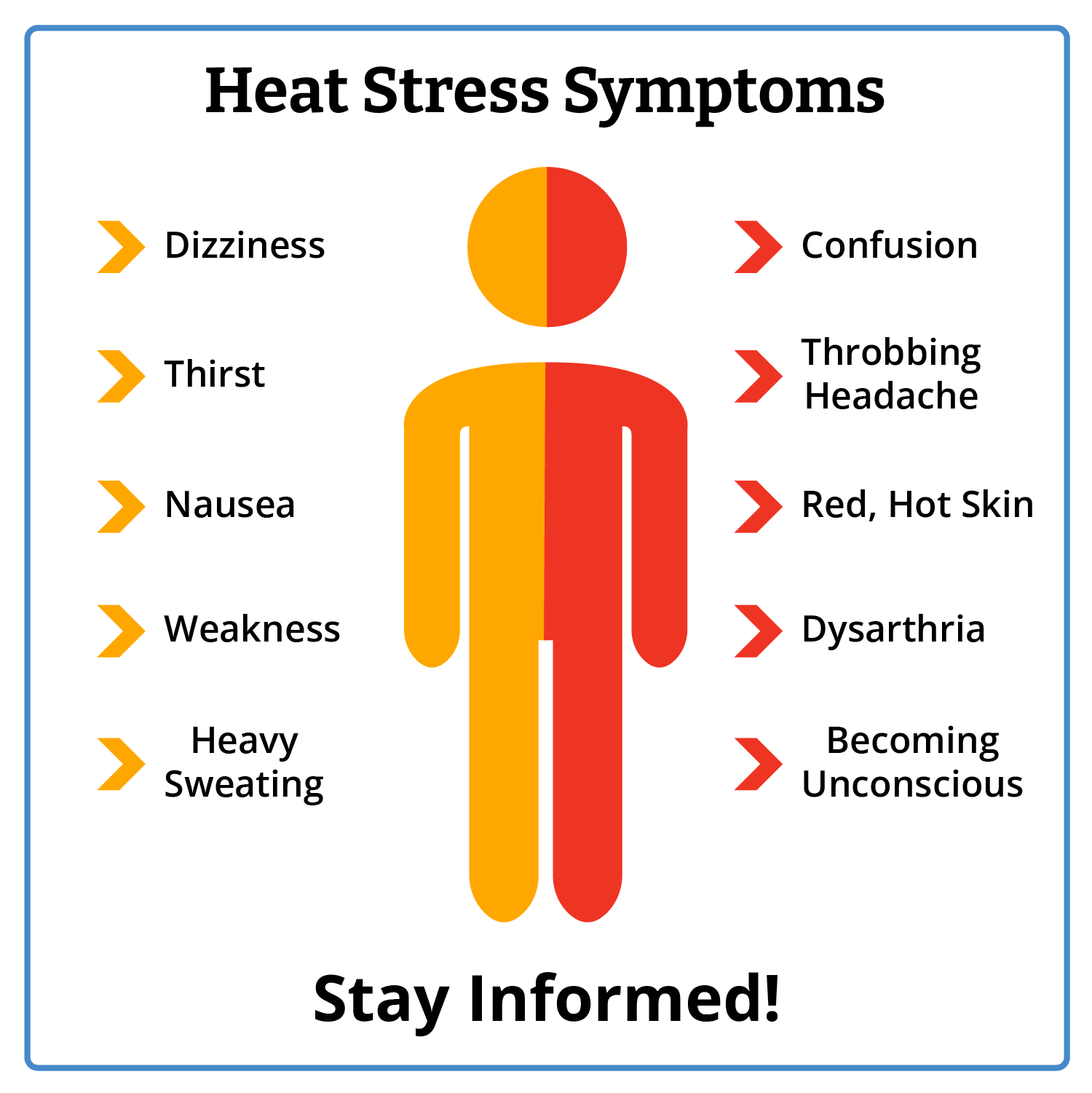
Recognizing the Signs of Heat Stress
Early recognition of heat stress symptoms is crucial for preventing more severe heat-related illnesses. Common signs include:
Heat Rash | Red clusters of small blisters or pimples that may be itchy. |
Heat Cramps | Painful muscle spasms, often in the legs or abdomen, caused by dehydration and loss of electrolytes. |
Heat Exhaustion | Symptoms include heavy sweating, weakness, dizziness, nausea, and a rapid heartbeat. |
Heat Stroke | A life-threatening emergency characterized by a high body temperature, confusion, loss of consciousness, & hot, dry skin. |
The Importance of Heat Stress Safety in the Workplace
Understanding heat stress is crucial, not only for the well-being of employees but also for maintaining a productive and safe work environment.
Employee Well-being and Productivity
Ensuring heat stress safety is not just a legal requirement; it’s a fundamental aspect of promoting a healthy workplace. When employees feel safe and comfortable, their overall well-being improves, leading to increased productivity and job satisfaction. Conversely, neglecting heat stress safety can result in reduced employee performance, increased absenteeism, and a higher risk of accidents and injuries.

Legal & Ethical Responsiblities
Employers have a legal and ethical responsibility to provide a safe working environment. Regulatory bodies such as the Department of Labor’s Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) establish guidelines and standards to address heat stress hazards in various industries. Non-compliance can lead to legal consequences, fines, and damage to a company’s reputation. By prioritizing heat stress safety, employers demonstrate their commitment to the well-being of their workforce and compliance with relevant regulations.
Implementing an Effective Heat Stress Program
Workplace Assessment
Before implementing a heat stress safety program, it’s crucial to conduct a thorough assessment of the workplace. Identify areas with high temperatures, evaluate humidity levels, and assess the physical demands of different tasks. This assessment will help tailor safety measures to the specific needs and challenges of the workplace.
Training & Awareness
Training is a cornerstone of any successful heat stress safety program. Ensure that employees, supervisors, and management receive comprehensive training on:
Heat stress risks & symptoms
Proper hydration practices
Use of PPE
Emergency response procedures
Regular refresher courses and ongoing awareness campaigns help reinforce safety practices and keep heat stress prevention at the forefront of everyone’s minds.
Proactive Environment Monitoring with Room Alert
Any business, facility or organization that is responsible for the safety and well-being of their employees should be concerned about monitoring their environmental conditions. Take a moment to think about the environmental conditions of your employees’ workplace. At just 80 degrees Fahrenheit (26 degrees Celsius), fatigue is possible with prolonged exposure and/or physical activity.
By installing Room Alert, you can stay in the know about heat and worker safety while following guidelines from government agencies and professional associations such as the CDC, EPA, ASHRAE and OSHA. Room Alert environment monitoring provides real-time data and alerts to help equip individuals and organizations with the ability to proactively address heat-related hazards, ensuring the safety and well-being of people and critical infrastructure.

What Employers Need To Know
Prioritizing heat stress safety in the workplace is not only a legal obligation but a critical aspect of creating a healthy and productive work environment. By implementing comprehensive safety measures, including training, awareness, and proactive environment monitoring, employers can significantly reduce the risk of heat-related illnesses. Employee involvement, education, and ongoing monitoring are key components of a successful heat stress safety program.
Remember, the well-being of your workforce is paramount. By taking proactive steps to address heat stress, you not only protect your employees but also contribute to a positive workplace culture and sustainable business success.

Room Alert has you covered for all your heat stress safety needs. If you have any questions or want additional information on installing Room Alert as a part of completing your heat stress safety program, please contact us today through email at Sales@RoomAlert.com, through our online Live Chat service, via phone at 888.220.6700, visit RoomAlert.com or AVTECH.com.